TextInput in GameActivity Part of Android Game Development Kit.
GameActivity integrates GameTextInput by:
- providing a wrapper
- creating a flag for new text input event availability
- directly using GameTextInput’s state buffer for the text content
As shown in the following diagram, applications use different internal logical components for user text input purpose:
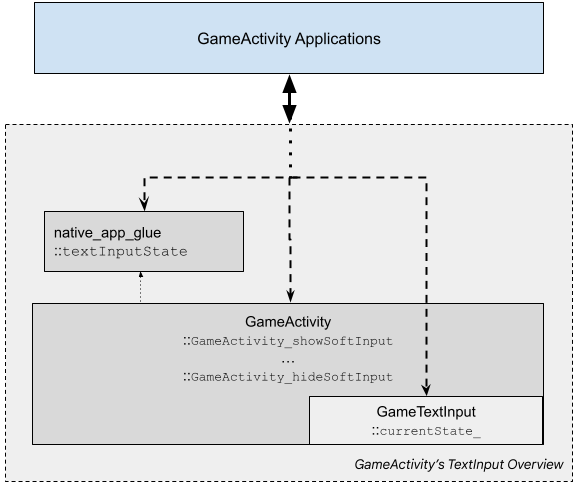
There are three broad steps to using the built-in GameTextInput library:
- Controlling the soft keyboard on UI
- Knowing when new text is available
- Retrieving the user input text and its states
The rest of this document describes them in detail. For an example of
GameTextInput with GameActivity in action, see the
games-samples repository.
Control the soft keyboard on UI
GameActivity provides two functions to control the soft keyboard on the UI:
GameActivity_showSoftInput()displays the soft keyboard.GameActivity_hideSoftInput()hides the soft keyboard.
Refer to the API reference docs for their definitions. After the keyboard is displayed, the application’s UI may look similar to the following:
Check for text availability
Soft keyboard events get passed from GameTextInput on the Java side to the
C/C++ side through the JNI, then travel up to GameActivity’s wrapper, finally
reflecting in the android_app::textInputState flag
implemented in native_app_glue. Applications
should poll this flag periodically to perform the intended processing:
- GameActivity only sets the
android_app::textInputStateflag. - Applications poll the flag and handle the new
GameTextInputevents, such as the new text added to the input buffer. - Applications clear the
android_app::textInputState.
Note that android_app::textInputState does not differentiate between single
and multiple text input events.
For a simple example, the following code polls the textInputState flag after
handling app cycle commands, touch events, and key events:
while (true) {
// Read all pending events.
int events;
struct android_poll_source* source;
while ((ALooper_pollOnce(engine.animating ? 0 : -1, nullptr, &events,
(void**)&source)) >= 0) {
// Process this event, etc.
...
// Check if we are exiting.
if (app->destroyRequested != 0) {
engine_term_display(&engine);
return;
}
}
engine_handle_input(app);
// Process text input events if there is any outstanding.
if (app->textInputState) {
// process TextInput events.
...
//reset the textInputState flag
app->textInputState = 0;
}
if (engine.animating) {
// draw frames.
}
}
Retrieve the user input text
The input texts and other states are accumulated in GameTextInput’s
internal buffer, GameTextInput::currentState_. Applications
can use one of the following ways to retrieve its content:
- GameActivity’s wrapper API (recommended)
- GameTextInput API
Get TextInput state with GameActivity API
Applications acquire the current text input with the typical callback mechanism:
- Implement a callback function of type
GameTextInputGetStateCallbackto process text input events. - Call
GameActivity_getInputState()when there is one or multiple outstanding events. - Clear the
android_app::textInputStateafter the events are processed.
Continuing with the snippet in the previous section, the following code acquires a reference to the text input buffer, processes it (not shown), and resets the event flag:
extern "C" void GameTextInputGetStateCB(void *ctx, const struct GameTextInputState *state) {
auto* engine = (struct engine*)ctx;
if (!engine || !state) return;
// Process the text event(s).
LOGI("UserInputText: %s", state->text_UTF8);
// Clear the text input flag.
engine->app->textInputState = 0;
}
In the game loop shown in the previous section, check and process text with the above text input handler:
if (state->textInputState) {
GameActivity_getTextInputState(
app->activity,
GameTextInputGetStateCB, // App's event handler shown above.
&engine // Context to the GameTextInputGetStateCB function.
);
}
Applications can optionally initialize the GameTextInputState content with
GameActivity_setTextInputState().
Get TextInput state with GameTextInput API
Applications can also directly use GameTextInput API to retrieve the current
GameTextInputState:
- Use
GameActivity_getTextInput()to get GameActivity’s internalGameTextInputinstance. - With the
GameTextInputinstance in hand, callGameTextInput_getState()to get the sameGameTextInputStatecontent.
Again, note that applications should not initialize GameTextInput
directly; GameActivity already does that during its initialization process.
The callback mechanism is the same as that used by the GameActivity’s
GameActivity_getTextInputState() function.
References
Developers might find the following resources helpful when creating
GameActivity applications:
- GameActivity get started
- GameTextInput user documentation
- agdkTunnel sample
- Jetpack reference documentation for GameActivity
- Jetpack reference documentation for GameTextInput
- AGDK source code
Feedback
GameActivity and GameTextInput are both part of Jetpack games library. For any issues and questions, create a bug on the Google IssueTracker.
