Getting started designing for Wear OS
Stay organized with collections
Save and categorize content based on your preferences.

Material Design for Wear OS helps you design engaging app experiences.
Understand use cases
Watches allow users to get information at a glance, such as seeing
progress towards health and fitness goals, and to act quickly, like responding
to an instant message. Focus on use cases like these when designing apps for
smartwatches.
The watch interface presents unique opportunities that are not available
on mobile devices, including:
- Input enabled by a physical body connection (through sensors and motion
detection).
- Quick access to glanceable information and actions, such as complications,
notifications, and Tiles.
The watch also comes with limitations:
- Smaller screen space
- Lower information density
- Limited battery life
Consider both the capabilities and limitations of the platform when designing
apps for watches.
check_circle
Do
Design experiences where tasks can be accomplished easily
using the watch interface.
cancel
Don't
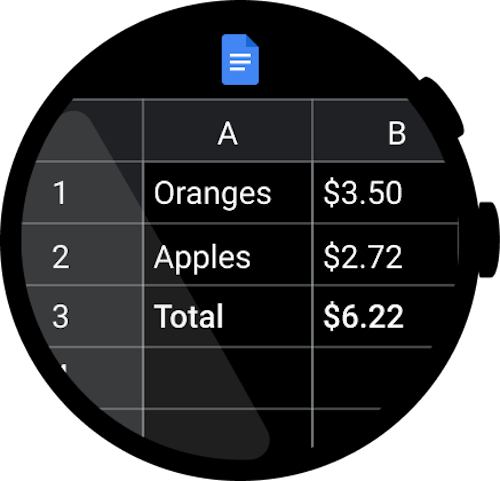
Don't create complex, detailed apps that include items like
spreadsheets, as this is difficult to edit and view on a watch.
Test designs
The majority of Wear OS devices have round screens, which have 22% less UI
space than square displays. Round screens also need larger margins for text to
be more readable.
Material Design for Wear OS helps you design engaging app experiences. The
following screenshots show a few illustrated examples of Wear OS apps that
follow the principles described in this guide.
check_circle
Do
Design for round devices first to make sure your layout works
within the smaller size constraints.
cancel
Don't
People wearing watches are regularly in motion, whether they
are standing, gesturing, or running to catch a bus. Test your designs in
situations that involve user movement to make sure the design is usable at
a glance.
App examples
Material Design for Wear OS helps you design engaging app experiences. The
following screenshots show a few illustrated examples of Wear OS apps that
follow the principles described in this guide.
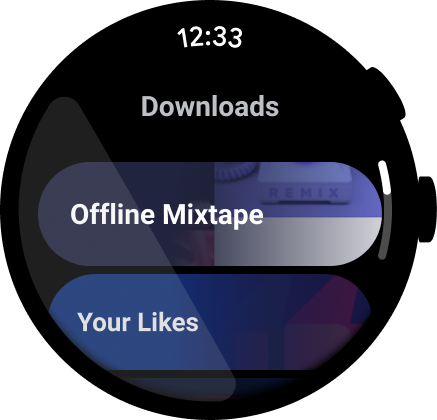
Figure 1. An example of a media app.
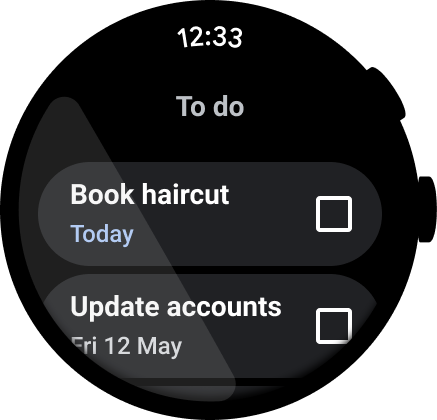
Figure 2. An example of a task management app.
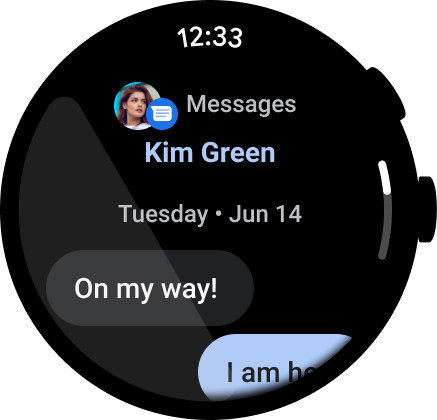
Figure 3. An example of an instant messaging app.
Figure 4. An example of a stopwatch app.
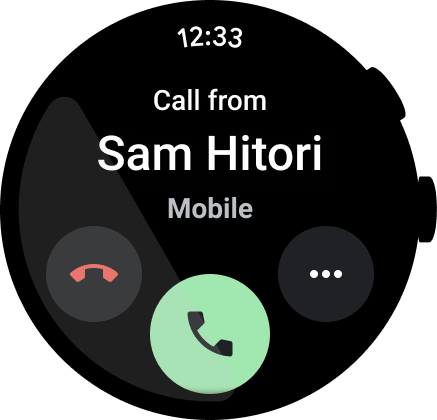
Figure 5. An example of a dialer app.
Figure 6. An example of a calculator app.
Content and code samples on this page are subject to the licenses described in the Content License. Java and OpenJDK are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2024-06-27 UTC.
[[["Easy to understand","easyToUnderstand","thumb-up"],["Solved my problem","solvedMyProblem","thumb-up"],["Other","otherUp","thumb-up"]],[["Missing the information I need","missingTheInformationINeed","thumb-down"],["Too complicated / too many steps","tooComplicatedTooManySteps","thumb-down"],["Out of date","outOfDate","thumb-down"],["Samples / code issue","samplesCodeIssue","thumb-down"],["Other","otherDown","thumb-down"]],["Last updated 2024-06-27 UTC."],[],[]]